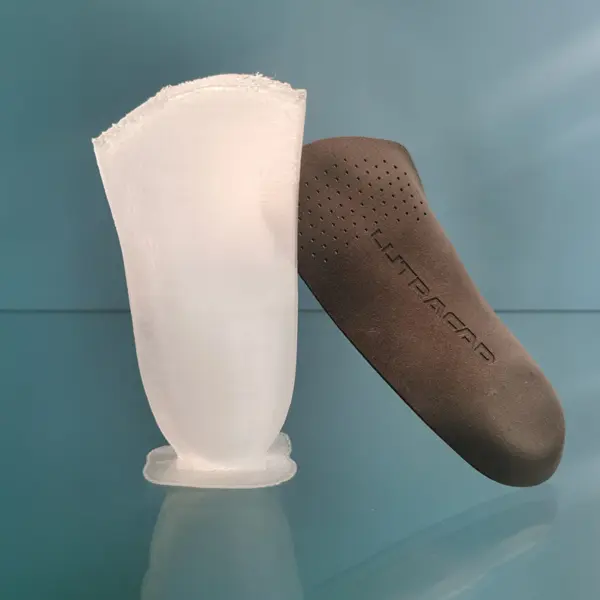
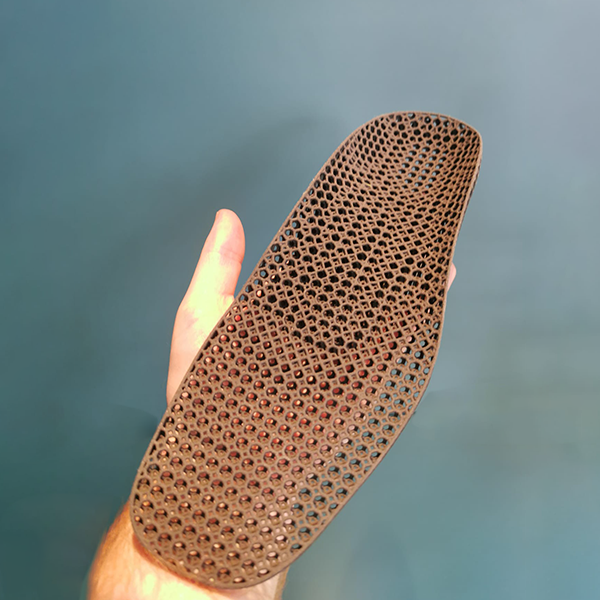
When it comes to custom insoles, the material choice makes a big difference. Some people prefer soft, cushioned insoles made from foam materials like EVA or foaming TPU (LutraCAD Nimbus). Others need the firm support of hard-shell insoles made from polypropylene (PP). Both have their strengths, but also their limits. Let's take a closer look.
Why Foam Insoles Are So Popular

Foam insoles are often the first choice when comfort comes first. They feel soft under the foot and help spread out pressure, which makes them very suitable for people who spend long hours standing or walking. The biggest advantage of foam is its comfort. It cushions the foot, reduces painful spots, and helps protect joints by absorbing shock.
Foam is also lightweight and flexible, so it doesn't make the shoe feel heavy or stiff. Materials like EVA can be milled, while TPU foams can be 3D printed, which means they can easily be shaped to match each person's foot. This makes them perfect for personalized insoles.
But foam also has some downsides. EVA and TPU are closed-cell materials, which means they do not let air pass through. This can make the feet feel warm or sweaty unless ventilation holes or covers are added. Foam also wears out faster than rigid materials – over time it can flatten, lose its bounce, or even tear. And while foam offers comfort, it does not give strong correction for serious foot problems.
In short: Foam insoles are all about comfort, shock absorption, and easy customization, but they are less durable and less supportive.
The Role of Hard-Shell Insoles
Hard-shell insoles made from polypropylene (PP) are very different. Instead of focusing on softness, they provide strength and correction. These insoles keep the foot in place and help correct biomechanical issues such as flat feet, overpronation, or posture problems. They are widely used in medical situations where stability and long-term control are needed.
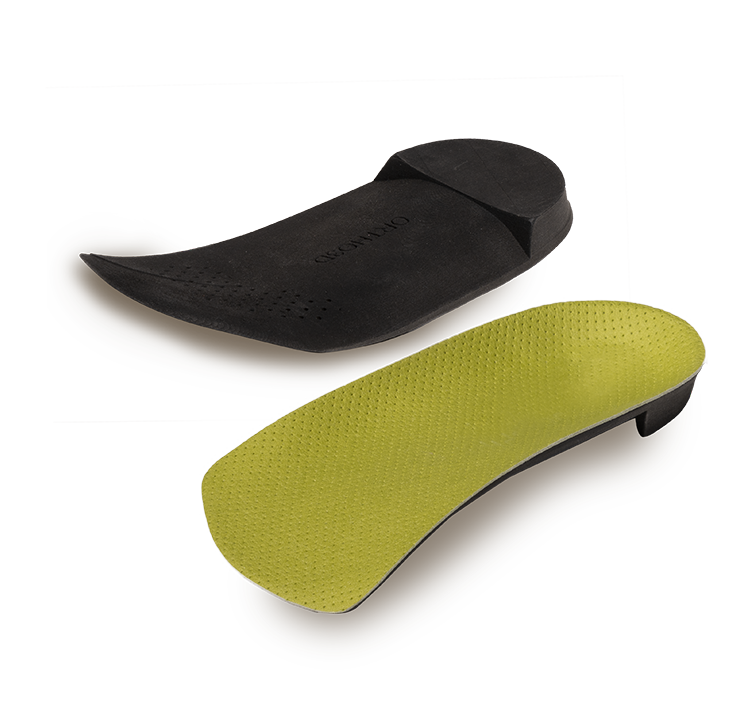

One of their biggest benefits is durability. Unlike foam, PP does not lose its shape or strength even after years of heavy use. It offers consistent correction every day. This makes PP insoles especially valuable for patients with diabetes, deformities, or other conditions where precision is very important.
Of course, there are also downsides. A PP insole without a soft top cover can feel hard and uncomfortable. It is also heavier and stiffer than foam, and it does not absorb shock very well. Adjustments can take more time, since the material is not as easy to reshape as foam.
So, hard-shell insoles are about correction, stability, and durability, but they lack comfort if used on their own.
The Best of Both Worlds
In many cases, there is no need to choose just one material. A very effective solution is to combine them: using a hard PP base for correction and stability, and adding a foam top for comfort and cushioning. This way, patients get the best of both – support where it is needed, and comfort where it matters most.
At LutraCAD, we don't believe in a one-size-fits-all approach. Our software allows you to design insoles in any material or combination, so you can choose exactly what your patients need. Whether it's the soft feel of foam, the strong control of polypropylene, or a layered mix of both, the design process is made simple and efficient.
Conclusion
- Foam insoles (EVA & TPU): Best for comfort, shock absorption, and daily wear. Great for people who stand or walk a lot, or for athletes.
- Hard-shell insoles (PP): Best for correction, stability, and long-term durability. Ideal for medical cases and patients with strong foot problems.
- Combination: Often the smartest choice – hard PP for correction and foam for comfort.
At LutraCAD, we don't believe in a one-size-fits-all approach. Our software is built to help you design with any material in mind, whether it's foam, rigid plastic, or a layered combination. The result? Insoles that do exactly what they're supposed to.
Ready to explore material possibilities?
Want to know more about material behavior in both 3D printing and milling? We're happy to help. Book a demo or get in touch!
Co-Founder of LutraCAD, I'm a passionate software developer with a keen interest in 3D printing. Merging technology with creativity, I'm dedicated to pushing the boundaries of design and innovation.
Tags: Accommodative Foam, Rigid Materials, 3D-printing,